The main
aspect in the context of the current challenge with the COVID-19 situation is
that ad hoc solutions are needed to keep companies operational. This includes
solutions for homeoffice as well as for meetings with customers and partners.
Regardless
of which technical solution is used, at the end of the day the common organizational
governance topics come up during the technical planning.
If users can decide individually and
independently to create new Teams and channels, invite external users and share
content, chaos results.
Who is supposed to organize this again
afterwards, and especially, who is supposed to decide which data and which
guestuser is still needed?
The fear of
this often prevents that Microsoft Teams is used. But in the current situation,
solutions and platforms like Microsoft Teams are needed to keep companies and
business running.
The Solution
Automated solutions to resolve governance topics such as data chaos, duplicates and orphaned guest accesses are the Azure features around the topics of Identity Governance and Lifecycle Management.
Entitlement Management
Azure AD Entitlement Management is an identity management feature-set that enables organizations to manage identity and access cycles by automating access request workflows, access assignments, reviews and expiration. The following graphic shows an example of the different elements of Azure AD Entitlement Management.

Access Package 1 includes a single Group as a
resource. Access is defined with a policy that allows users from a specific
Azure AD group to request access.
Access Package 2 includes a Group, an Application and
a SharePoint page as resources. Access is defined by two different policies.
The first policy allows a group of users in the directory to request access.
The second policy allows users from another / external Azure AD to request
access.
When an access package is created, we can defines how long
the access remains active before it is deactivated again:
An individual access URL is generated for each package.
Users then use this to activate the package for themselves:
Access Reviews & Groups Expiration Policies
Azure AD Access Reviews automate the regular review of group memberships, access to enterprise applications and role assignments. This ensures that only those people who need it continue to have access.
Overview:
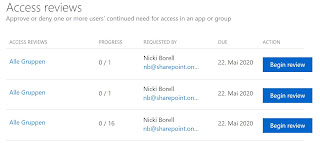
When an
Access Review is created, a user is assigned who must perform the review. This
can also be done dynamically based on the Groups / Teams Owner. The reviewer
then receives an e-mail that directs him to his upcoming reviews:
The
example shows that the first two groups each have only one member and were
probably created for test purposes only. The third group has 16 members.
Clicking the Begin review button will show the details and the
automatically generated recommendations:
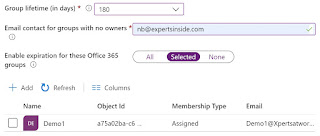
Groups
Expiration Policies are not shown in the Identity Governance section and must
be accessed via Azure AD -> Groups -> Expiration:
Again, the group owner receives a mail in which he must
confirm that the Group is still needed. If he does not do it, the Group is
automatically deleted. If a Group is deleted, it is "soft-deleted".
This means that it can be restored by an administrator for up to 30 days.
Further options
If all this is not sufficient to implement necessary requirements, there are extended possibilities with the features Azure AD Conditional Access and the feature App Management.
Conditional Access controls access to applications based on specific conditions. Conditional access policies are used to implement access control based on the specific context.
Example:
- Microsoft
teams can only be accessed from a company device.
- E-Mail
can be accessed from any device. However, if access is from outside the
corporate network, multi-factor authentication is enforced.
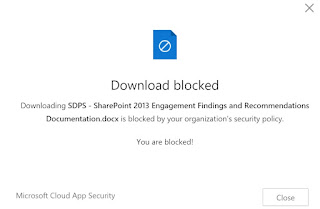
App Management (MAM) focuses on compliance with data
security policies and data protection requirements as well as actions in case
of data loss.
Example:
- Data
from Microsoft Teams is not allowed to be included in the iOS or Android
backup.
- Access
with a "jailbroken device" is blocked.
MAM without device registration or MAM-WE (WE=without
enrollment) allows IT administrators to manage apps on devices that are not
registered in Intune MDM.
Best Practis
At the end, it is not a question of what Azure features and functions are available, but rather what is to be achieved and what exactly the business case looks like. Therefore, start with your scenarios. The second step is then the mapping to the Azure features in order to implement the necessary governance aspects.