Site
classification is a must-have when we talk about Governance, Compliance and
also topics around GDPR.
Beside 3rd party solutions focusing on site
and content classification we have also some out of the box options and
developer opportunities in Office 365 and SharePoint on-prem. Depending on if
we are talking about classic SharePoint Site Collections or if we talk about modem
Team Sites, being part of an Office 365 Group, we have different szenarios.
To create a new SharePoint site in Office 365 we know two different ways.
- We can create a SharePoint Online Site using the SharePoint Online Administration. This will create a SharePoint Site based on WebTemplate STS
- We can go to SharePoint Home and click “create” in the upper left corner or we can go to Outlook Online and create a new Group. Both will create a SharePoint Site based on WebTemplate GROUP
- Define and set site policies
- Insert a custom action
- Custom site classification
- Add a classification indicator to site page
Using the opportunities
we have with Groups and Group Policies some of these things can be automatically
put to a SharePoint Site based on WebTemplate GROUP.
This video by Vesa Juvonen is showing the steps and
the final results:
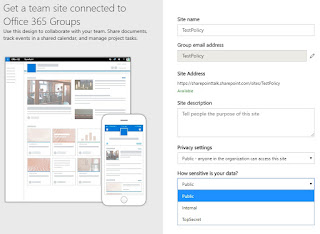
As you can
see we need to create the site bases on option 2.
(Dialogs already
including policies)
SharePoint Home - Create:
Outlook
Online -> Create Group:
Final
result:
Step by Step
To enable
this functionality in Office 365 we need to set up an “Settings Object” and a “Settings
Template” in Azure AD. To do this we can use the Azure
Active Directory cmdlets for configuring group settings.
First of
all we need to install the preview of Azure Active Directory V2 PowerShell
Module:
Install-Module -Name AzureADPreview
To set up the site
classification options and configure properties like ClassificationList and ClassificationDescriptions etc follow these steps also shown in Vesas video:
#Connect
Connect-AzureAD
Get-AzureADDirectorySettingTemplate
#Create
$Template = Get-AzureADDirectorySettingTemplate -Id
62375ab9-6b52-47ed-826b-58e47e0e304b
$Setting = $template.CreateDirectorySetting()
$setting["UsageGuidelinesUrl"] =
"http://sharepointtalk.com"
$setting["ClassificationList"] = "Public, Internal,
TopSecret"
$setting["DefaultClassification"] = "TopSecret"
$setting["ClassificationDescriptions"] = "Public:no
restrictions,Internal:all internal users can access,TopSecret:only special
users can access"
$setting["GuestUsageGuidelinesUrl"] =
"http://sharepointtalk.net"
New-AzureADDirectorySetting -DirectorySetting $setting
#Check
Get-AzureADDirectorySetting -All $True
(Get-AzureADDirectorySetting -Id %%YOUR
ID%%).values
As described in the
video we can now use the CLASSIFICATION property to assign a site policy or any
other custom action. Details about site policies are part of Implement
a SharePoint site classification solution.
Here the script taken
from the video to get the CLASSIFICATION property:
#Get PnP PowerShellOnline
Install-Module SharePointPnPPowerShellOnline
#Get Site classfication value
Connect-PnPOnline https://%YOUR TENANT%.sharepoint.com/sites/%YOUR SITE%
Get-PnPSite
$Site.Classification
Get-PnPProperty
-ClientObject $Site -Property Classification