PART II: What happens with
FAST in SharePoint 2013
(Concern that this is BETA stuff. Features and
functions can be changed or shift until the final release!)
Fact 1: In SharPoint 2013 the two Search Engines “SharePoint
Search” and “FAST Search Server for SharePoint” was combined in one Search
Engine.
Fact 2: FAST as a standalone product is still available and
supported. Details see here: http://support.microsoft.com/lifecycle/search/default.aspx?sort=PN&alpha=fast
Future of FAST ESP: See this statement from Rob Va from July 16: http://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/fastinternetesp/thread/86e5e64f-1fd0-4ee4-a025-1dea0f1693df
Mostly all the
features / functions that we know from FAST Search Central Admin sites had been integrated in Enterprise Search in
SharePoint 2013:
Let’s have a look at
the feature and functions level:
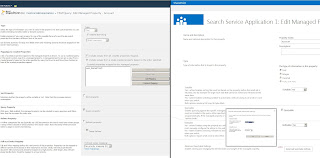
Managed Properties:
The technique with
crawled properties and managed properties was similar in SharePoint Enterprise
Search and FAST Search Server for SharePoint. But with FAST we had additional configuration
options:
The functions / fields: Name, Type and Mappings to Crawled Properties were the same in both SharePoint 2010 Search Engines.
The
features Sort Property, Query Property, Refiner Property and Full-text Index
Mapping moved into the new Managed Property
configuration:
There are
some more options in the new SharePoint 2013 Managed Property configuration,
but this will be part of “Part IV:
Admin Stuff”.
Crawled
Properties:
Crawled
Properties are the same in FAST, Enterprise Search, and SharePoint 2013 Search.
Managed
Property Extraction:
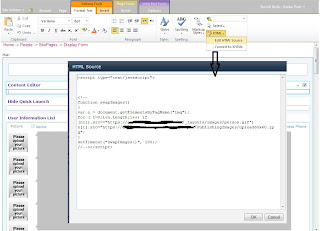
This section
was completely reworked. In FAST 2010 we have to work with some PowerShell
calls like: Get-FASTSearchResource dictionaries\spellcheck\sk_spell_iseck_en.txt and dictionary files based on an
XML structure to include new terms. In SharePoint 2013 this feature used the
Managed Metadata / Termstore to handle the term / dictionaries for company
individual property extraction:
You can see
that the function for ignore list and spell checking also moved to the Termstore. In detail we will have a look at this in Part III.
FAST
Service Application:
So in
fact only one integrated Search Engine left we didn’t have to configure the
different Shared Service Applications for FAST Contend and Fast Query as we
have to in SharePoint 2010:
Query
Language / FAST Query Language:
FAST
brings his own Query Language which was just different / extended from the
SharePoint Search Query Language. Some of its characteristics are now found
into Search Query Language. For example the XRANK Operator:
In SharePoint Server 2010, the XRANK operator
was available only with FAST Query language (FQL). The XRANK operator provides
dynamic control of ranking.
SharePoint
2013 Search does not longer support SQL syntax. Search in SharePoint 2013 supports
FQL syntax and KQL syntax for custom search solutions.
For more
details about building Search Querys ins SharePoint 2013 Search have a look
here:
FAST
Stuff:
FAST
stuff and FAST specific components like the “extended WebCrawler” or commanding
tools like indexerinfo.exe are no longer part of SharePoint, at least
not part of the SharePoint 2013 Preview version.
Developing custom connectors / crawler is now standardized.
Content Processing:
In FAST for SharePoint 2010 we had the Advanced Content Processing Pipeline
architecture:
In SharePoint 2013
this is part of the common Search Architecture.
Next parts in this
series:
Part III: A look in the deep
what’s behind the new Search functions like “Search Dictionaries”, “Query
Builder”, “Query Client Type”
Part IV: Admin Stuff
Part V: Frontend Stuff


















.jpg)